Telemedicine IoT Integration: Home Healthcare Technology
Discover how telemedicine IoT integration transforms home healthcare with smart devices, remote monitoring, and connected medical technology solutions.
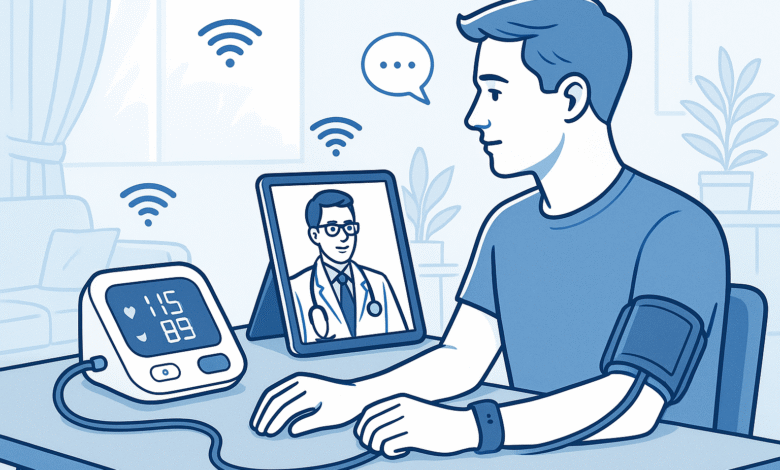
The healthcare landscape is changing rapidly, and telemedicine IoT integration is leading this transformation. This powerful combination of remote medical care and smart connected devices is making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and personalized than ever before. From monitoring vital signs at home to enabling real-time consultations with doctors, this technology is reshaping how we think about medical care.
What is Telemedicine IoT Integration?
Telemedicine IoT integration combines remote healthcare services with Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create a seamless healthcare experience. This technology allows patients to receive medical care from the comfort of their homes while providing healthcare providers with real-time health data through connected medical devices.
The integration works by connecting various smart health devices – like blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and heart rate sensors – to healthcare platforms that doctors can access remotely. This creates a continuous flow of health information that helps medical professionals make better treatment decisions without requiring patients to visit clinics frequently.
Remote patient monitoring has become a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery. By using connected medical devices, healthcare providers can track patient health metrics continuously, detect early warning signs of health issues, and intervene quickly when necessary. This proactive approach to healthcare management leads to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Key Components of IoT Healthcare Systems
Smart Medical Devices
The foundation of any telemedicine IoT integration system lies in smart medical devices. These devices collect vital health information and transmit it securely to healthcare providers. Common examples include:
Wearable health monitors track everything from heart rate and sleep patterns to physical activity levels. These devices provide continuous health monitoring without interfering with daily activities. Popular wearables can detect irregular heartbeats, monitor blood oxygen levels, and even predict potential health emergencies.
Home diagnostic tools allow patients to perform basic medical tests at home. Digital thermometers, blood pressure cuffs, and glucose monitors can now connect to smartphones and automatically share results with healthcare teams. This eliminates the need for manual recording and reduces the chance of human error in data collection.
Chronic disease management devices help patients with conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease monitor their health more effectively. These devices can send alerts when readings fall outside normal ranges, prompting patients to seek medical attention or adjust their treatment plans.
Connectivity Solutions
Reliable connectivity is essential for effective telemedicine IoT integration. Healthcare IoT devices use various connection methods including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and specialized healthcare communication protocols. The choice of connectivity depends on factors like device location, data transmission requirements, and security needs.
Cloud-based healthcare platforms serve as the central hub for collecting, storing, and analyzing health data from multiple devices. These platforms use advanced analytics to identify trends, predict health issues, and provide actionable insights to both patients and healthcare providers.
Data Analytics and AI
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play crucial roles in processing the vast amounts of health data generated by IoT devices. These technologies can identify patterns in patient data that might not be obvious to human observers, enabling early detection of health problems and more personalized treatment approaches.
Predictive analytics helps healthcare providers anticipate patient needs and potential health complications before they become serious. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions that can prevent hospitalizations and improve patient outcomes.
Benefits of Home Healthcare Technology
Improved Patient Outcomes
Telemedicine IoT integration significantly improves patient outcomes through continuous monitoring and early intervention. When healthcare providers have access to real-time health data, they can detect problems early and adjust treatment plans quickly. This leads to better disease management, fewer emergency room visits, and improved overall health.
Remote patient monitoring is particularly beneficial for managing chronic diseases. Patients with diabetes can track their blood sugar levels throughout the day, while those with heart conditions can monitor their cardiac rhythms continuously. This constant oversight helps prevent serious complications and hospitalizations.
Enhanced Accessibility
One of the most significant advantages of home healthcare technology is improved access to medical care. Patients in rural areas, those with mobility issues, and individuals with busy schedules can receive quality healthcare without traveling to medical facilities. This democratization of healthcare ensures that more people can receive the medical attention they need.
Virtual consultations through telemedicine platforms allow patients to speak with healthcare providers from anywhere with an internet connection. This convenience factor has made healthcare more accessible to millions of people who previously faced barriers to receiving medical care.
Cost-Effective Healthcare
Telemedicine IoT integration reduces healthcare costs for both patients and providers. Patients save money on travel expenses, time off work, and facility fees. Healthcare systems benefit from reduced overhead costs, more efficient use of medical staff time, and decreased need for expensive emergency interventions.
The ability to monitor patients remotely also reduces the length of hospital stays and the frequency of readmissions. When patients can be safely monitored at home while recovering from procedures or managing chronic conditions, it frees up hospital resources for more critical cases.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Connected medical devices provide healthcare providers with detailed, personalized health data that enables more targeted treatment approaches. Instead of relying on periodic snapshots of patient health during office visits, doctors can see how patients respond to treatments over time and make adjustments based on real-world data.
This personalized approach to healthcare management leads to better treatment compliance, improved patient satisfaction, and more effective medical interventions.
Popular IoT Healthcare Applications
Chronic Disease Management
Telemedicine IoT integration excels in managing chronic conditions that require ongoing monitoring and treatment adjustments. Diabetes management systems combine glucose monitors, insulin pumps, and mobile apps to help patients maintain optimal blood sugar levels. These integrated systems can automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings and lifestyle factors.
Heart disease monitoring systems use connected devices to track blood pressure, heart rhythm, and other cardiac markers. When abnormal readings are detected, the system can alert both patients and healthcare providers immediately, enabling quick responses to potentially dangerous situations.
Post-Surgical Recovery
After surgery, patients often need close monitoring during their recovery period. IoT-enabled recovery monitoring systems allow patients to heal at home while providing healthcare teams with the data they need to ensure proper healing. These systems can track vital signs, pain levels, and wound healing progress without requiring frequent hospital visits.
Smart bandages and wound monitoring devices can detect signs of infection or poor healing, alerting healthcare providers to intervene before complications develop. This technology has significantly reduced post-surgical complications and improved patient satisfaction with the recovery process.
Mental Health Support
Digital therapeutics and mental health monitoring represent growing applications of telemedicine IoT integration. Wearable devices can track physiological indicators of stress, anxiety, and depression, providing objective data to support mental health treatment decisions.
Smartphone apps integrated with IoT sensors can monitor sleep patterns, physical activity, and social interactions – all important factors in mental health management. This data helps mental health professionals understand how environmental and lifestyle factors affect their patients’ wellbeing.
Elderly Care and Independent Living
Senior care has been transformed by home healthcare technology. Smart home systems can monitor elderly individuals’ daily activities, detect falls, and alert caregivers to potential emergencies. These systems help seniors maintain their independence while providing family members and healthcare providers with peace of mind.
Medication adherence monitoring systems ensure that elderly patients take their medications correctly and on time. Smart pill dispensers can send reminders, track medication usage, and alert caregivers if doses are missed.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Data Security and Privacy
Healthcare data security remains one of the biggest challenges in telemedicine IoT integration. Patient health information is highly sensitive and must be protected according to strict regulatory requirements. Healthcare organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures including encryption, secure authentication, and regular security audits.
HIPAA compliance is mandatory for all healthcare IoT systems in the United States. This requires careful attention to how data is collected, transmitted, stored, and accessed. Healthcare organizations must work with technology partners who understand these requirements and have proven track records in healthcare data security.
Technical Integration Issues
Integrating multiple IoT devices with existing healthcare systems can be technically challenging. Different devices may use different communication protocols, data formats, and security standards. Healthcare organizations need comprehensive integration strategies that ensure all devices work together seamlessly.
Interoperability standards help address these challenges by providing common frameworks for device communication and data exchange. Healthcare organizations should prioritize solutions that adhere to established interoperability standards to ensure long-term compatibility and scalability.
Patient Education and Adoption
Successful implementation of home healthcare technology requires patient education and support. Many patients, particularly older adults, may be hesitant to adopt new technologies or may need help learning how to use IoT devices effectively.
Healthcare organizations should provide comprehensive training programs, user-friendly device interfaces, and ongoing technical support to help patients successfully adopt and use home healthcare technologies. Clear communication about the benefits and proper use of these systems is essential for achieving high patient adoption rates.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare IoT systems must comply with various regulatory requirements that vary by country and region. In addition to data privacy regulations, medical devices must meet safety and efficacy standards established by regulatory bodies like the FDA in the United States.
Healthcare organizations should work with experienced partners who understand the regulatory landscape and can help navigate the approval and compliance processes for healthcare IoT implementations.
Future Trends in Telemedicine IoT Integration
Advanced AI and Machine Learning
The future of telemedicine IoT integration will be shaped by increasingly sophisticated artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These technologies will enable more accurate health predictions, personalized treatment recommendations, and automated health interventions.
AI-powered diagnostic tools will become more prevalent, helping healthcare providers identify health issues earlier and with greater accuracy. Machine learning algorithms will continuously improve their ability to analyze complex health data patterns and provide actionable insights.
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance the capabilities of healthcare IoT systems. Faster data transmission speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity will enable real-time health monitoring applications that weren’t previously possible.
5G will support more sophisticated telemedicine applications including high-definition video consultations, real-time surgical guidance, and immediate transmission of large medical imaging files.
Expanded Device Ecosystem
The ecosystem of connected health devices will continue to expand, covering more aspects of health and wellness. New sensors and monitoring technologies will provide deeper insights into patient health, while improved battery life and miniaturization will make devices more convenient to use.
Smart contact lenses that monitor intraocular pressure, implantable sensors that track medication levels, and advanced wearable devices that monitor multiple biomarkers simultaneously are just some of the innovations on the horizon.
Integration with Smart Cities
Telemedicine IoT integration will increasingly connect with broader smart city initiatives. Environmental monitoring systems will provide data on air quality, noise levels, and other factors that affect public health. This integration will enable more comprehensive approaches to population health management.
Smart city healthcare networks will coordinate emergency response systems, optimize healthcare resource allocation, and provide real-time health information to support public health decision-making.
Getting Started with Home Healthcare Technology
Choosing the Right Devices
Selecting appropriate IoT healthcare devices depends on specific health needs, technical capabilities, and budget considerations. Patients should work with their healthcare providers to identify which monitoring capabilities would be most beneficial for their health conditions.
Key factors to consider include device accuracy, ease of use, battery life, connectivity options, and integration with existing healthcare systems. It’s important to choose devices from reputable manufacturers that prioritize data security and regulatory compliance.
Setting Up Your System
Proper setup is crucial for successful telemedicine IoT integration. This includes ensuring reliable internet connectivity, downloading necessary mobile apps, and configuring devices according to manufacturer instructions. Healthcare providers should offer setup assistance and technical support to help patients get started successfully.
Regular maintenance and updates are important for keeping healthcare IoT systems functioning properly. Patients should understand how to perform basic troubleshooting and know when to contact technical support for help.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Effective use of home healthcare technology requires good communication and collaboration with healthcare providers. Patients should understand how their data will be monitored, what types of alerts or interventions to expect, and how to respond to system notifications.
Healthcare teams should establish clear protocols for data monitoring, patient communication, and emergency response procedures. Regular check-ins and system reviews help ensure that the technology is meeting patient needs and achieving desired health outcomes.
Conclusion
Telemedicine IoT integration represents a fundamental shift toward more accessible, efficient, and personalized healthcare delivery. By combining remote medical services with smart connected devices, this technology is making it possible for patients to receive high-quality healthcare from their homes while providing healthcare providers with the real-time data they need to deliver better care.
The benefits of home healthcare technology extend beyond convenience – they include improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and better management of chronic diseases. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that further transform how healthcare is delivered and experienced.
Success in implementing telemedicine IoT solutions requires careful attention to data security, patient education, and system integration. Healthcare organizations that invest in comprehensive strategies addressing these challenges will be best positioned to realize the full benefits of this transformative technology.
The future of healthcare is becoming increasingly connected, personalized, and patient-centered. Telemedicine IoT integration is at the forefront of this transformation, offering new possibilities for improving health outcomes while making healthcare more accessible to people around the world. As these technologies continue to mature and expand, they will play an increasingly important role in creating a more effective and equitable healthcare system for everyone.